Multi-species grazing isn’t just about diversifying your operation and making good use of your pastures. It can also be a way to protect small ruminants from predation!
Flerd:
1. A contraction of flock and herd.
2. A mixed-species group of animals that consistently stays together under free-range conditions.
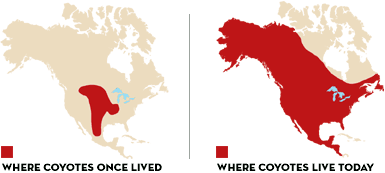
Losing animals to coyotes is no longer just a western problem. These two maps from the National Wildlife Federation show how coyotes have expanded their range. No matter where you live, even in urban areas, coyotes might be looking to snack on your small ruminant, or your cat or dog.
When the Jornada Experimental Range (JER) outside of Las Cruces, New Mexico expanded their range livestock research program to include sheep alongside cattle, they ran into a problem that anyone raising small ruminants has encountered: predators, mostly coyotes, began picking animals off. In fact, they lost 66% of the herd, dropping from 96 to 33 sheep in just one year. As Dean Anderson wrote in his 1998 paper in the Journal of Arid Land Studies, this catapulted them into predator control research. They ended up with a two-pronged approach that all but eliminated predation by coyotes. The solution? They got guard dogs to stay with the herd, and they taught the sheep to stay with the cows. The researchers started with two observations. First, free-ranging sheep don’t normally stay with cattle in the same pasture. In fact they interacted less than 6% of the time. Second, they had seen how aggressive cattle could be towards dogs, especially when they felt threatened. They figured that this aggression towards threatening dogs would translate to coyotes as well, and that if the sheep behaved as part of the cow herd, they’d have more protection. And with that, they began to figure out the logistics for bonding sheep, goats and cattle.

Here’s a 1987 JER picture showing bonding in progress. The sheep do not bond to an individual cow but to the species in general.
Pen Bonding
They started by penning young lambs with cattle for 3o days. All were fed together, though there was a creep to allow the lambs to escape to a safe place if necessary. That’s about all it takes, for sheep to bond to cattle. Further research has revealed that a good bond can be achieved in just 14 days, making it easier to get started flerding.
As all good researchers do, Dean Anderson and the folks at JER did a test to see if they were getting the results they hoped for. It involved sending a trained herding dog to round up cattle and sheep while they filmed what happened. The dog had a hard time with the control group because the sheep refused to move with the cattle, and ran off by themselves. The job was much easier for the dog when it came to trying to move the flerd. The sheep moved with the cattle, generally traveling in the midst of them, and the cattle did their job of occasionally turning on the dog to protect themselves and the sheep by extension. It’s easy to see from Dean Anderson’s 1987 video of the test that flerds provide a lot of protection to sheep and goats.
Here’s the link for tablet folks.
The biggest issue/expense in creating a flerd is feeding the animals while they’re bonding. Fortunately, you don’t have to train every member of your flock. By taking advantage of the flocking instinct of your small ruminants you can provide protection to unbounded animals. Bonded animals, will stick with the cattle, and those without a bond to cattle will stick with their flock mates. Jornada researchers found that 12 bonded sheep controlled the movements of 12 non-bonded sheep. You can see this at work in Dean Anderson’s video below.
Here’s the link for tablet folks.
At the Jornada Experimental Range, researchers use this herd behavior to introduce new lambs to the flerd. Ewes are removed from the range to give birth in a corral where they remain for about 2 months while the lambs grow and gain strength. Then the ewes and lambs go back on the range with their cattle flerd. Though the lambs spend about 3 months with the cattle as part of the flerd, the bonding process doesn’t really seem to begin for them until after weaning. It’s possible that they are simply too focuses on their bond with their mothers. After weaning, as they continue to follow their mothers and the flerd, the bond begins to form. After 217 days with the flerd, their bond with cattle is as strong as pen-bonded lambs that spent 34 days with heifers before joining the herd.
Flerd Benefits
There are management and pasture benefits to be gained by running sheep and cattle together. Sheep-proof fences on the range are no longer required because the sheep will stay with the cattle. Any fencing that will keep cattle in a particular pasture will keep the sheep with them, as long as their are no cattle in the adjacent pasture. Sheep aren’t bonded to a particular cow or herd, they are bonded to all cattle, so will move to other cattle readily given the opportunity. It’s also easier to find your small ruminants on large ranges, in dense brush or in fog or snow because the size of the cows makes the group easier to see. Finally, cattle tend to range over a larger area when foraging than sheep and other small ruminants. Sheep in flerds stick with the cattle, distributing foraging over a larger area than possible with just a flock.
It’s also important to note that flerding replaced other ways of trying to prevent coyotes from eating sheep. Before flerding Anderson says “we relied on gunning, trapping, snares, electrified fences and guarding dogs.” Post-flerding, they only used Turkish Akbash guard dogs.
Ready to Give Flerds a Shot? Here Are Some Tips
1) Use sheep and goat breeds that exhibit flocking tendencies. Researchers found that white face sheep breeds may bond better than black face breeds based on their flocking tendencies. They also found that spanish goats could bond, but that over time, they became less bonded and wandered away from the herd more.
2) Younger animals bond better than older animals. Researchers have done this with 1 day old lambs, and with yearling ewes with good results. Jornada researchers were successful with lambs 45, 62, and 90 days old as well as with 18 month old ewes.
3) Any age docile cattle will do, but keep in mind that heifers eat less than a full grown cow and will reduce the costs of the bonding process. If you find a cow abusing lambs, remove it immediately because there’s no way to make lambs bond with their abusers.
4) Bond strength is measured by how far sheep stray from the cattle. The stronger the bond, the shorter the distance between sheep and cattle. Bonds can be created in as little as 14 days.
5) Pens should be in quiet areas with little activity. The size of your pen will determine the ratio of cattle to sheep for the training. In smaller pens (52 square feet per animal), Jornado researchers used one cow per 3 lambs, and in larger pens, (188 square feet per animal) they used one cow per lamb.
6) Provide a creep area for the small ruminants as a place to escape if threatened, and to provide supplemental feed for growing lambs and kids. Feed hay on either side of the creep for the first 24 to 72 hours so animals can see each other, yet lambs have some degree of safety as they get to know the larger cattle.
7) Consider putting bells on some cattle during training. Lambs will learn that the sound is associated with where they ought to be, and help orient them in larger pastures.
Read More About It
Here are published papers on this subject:
Pro-active Livestock Management — Capitalizing on Animal Behavior
Dean Anderson, Journal of Arid Land Studies, 1998
Flocks and Herds or Flerds – It’s Your Choice
Dean Anderson, Grassroots: Newsletter of the Grassland Society of Southern Africa, June 2004, Vol 4 No 2
Pen confinement of yearling ewes with cows or heifers for 14 days to produce bonded sheep
E.L. Fredrickson, D.M. Anderson, R.E. Estell, K.M. Havstad, W.L. Shupe, M.D. Remmenga, Small Ruminant Research 40 (2001) 291-297
 Print
Print Email
Email





